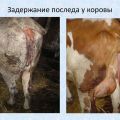
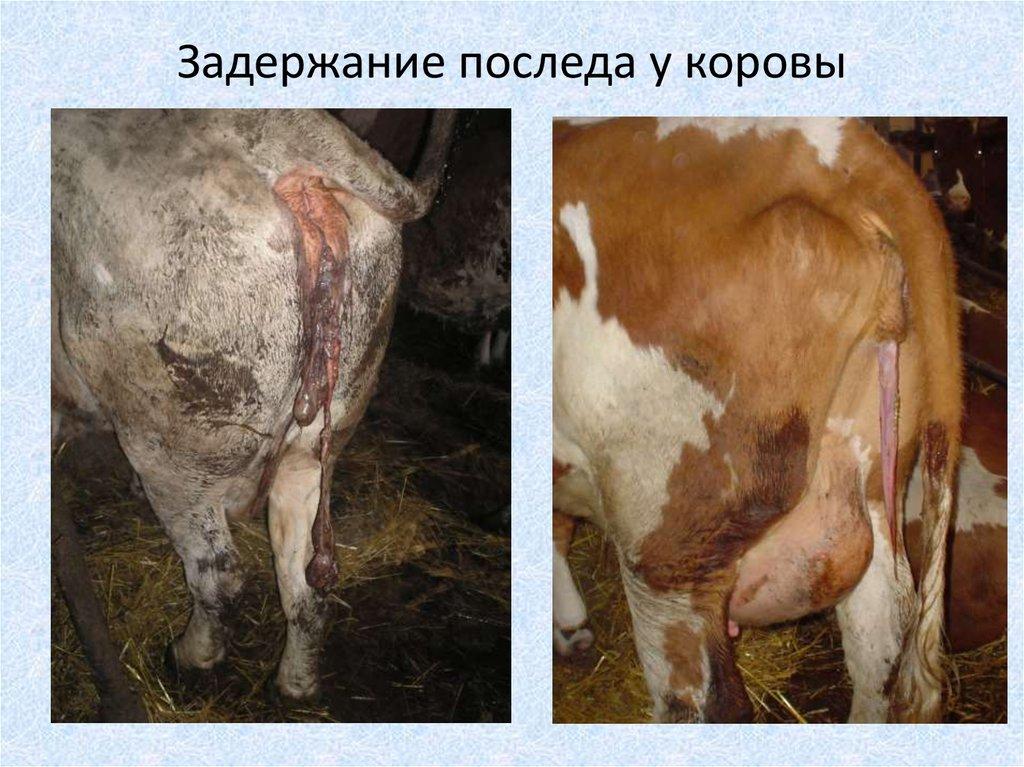
What does the afterbirth look like in a cow and how long does it take, what if it hasn't left
The opinions of veterinarians about how long the afterbirth normally takes in a cow is still different. Someone thinks that you should not panic if the placenta has not left within three days, others recommend waiting a day and taking action. Coming to the general opinion, experts warn that the placenta should leave 12 hours after calving. If this does not happen, the cow needs help to avoid serious health consequences and even death.
What makes the delay
In many literary sources it is written that the release of the membranes after calving should occur in the cow no later than 12 hours, while the delay in the release of the placenta by 8-9 hours, in most cases, requires the intervention of a specialist. In old-born cows and bearing several calves at once, this time can be extended to 16 hours.
The reasons why the afterbirth does not go away on its own may be as follows:
- insufficient uterine tone or complete cessation of organ contractions - arises from insufficient physical activity of the cow. If an animal walks less than 10 kilometers per day, muscle tissue relaxes, including uterine tissues. As a result, the organ cannot independently expel the membranes;
- obesity and metabolic disorders - are observed as a result of overfeeding, the predominance of sour pulp, sour corn, silage in the cow's diet;
- deficiency of vitamins and nutrients - calcium, phosphorus, selenium and vitamin E;
- protracted labor - more often the afterbirth does not go away on its own if two calves are born or one, but too large fetus, especially if it is incorrectly located in the uterus;
- too frequent childbirth, leading to excessive stretching of the muscles of the uterine walls;
- systemic diseases (brucellosis, vibriosis) that cause turgor of caruncles;
- infectious pathologies in the tissues of the uterus and amniotic fluid (chorion), leading to fusion of the fetal part with the maternal part of the placenta.
In order for the placenta to go away on its own, the full maturity of the placenta is important. With a lack of the hormone estrogen, which is responsible for the maturation of the placental tissue, problems arise with the separation of the membranes, more often in young cows and heifers.
Signs and symptoms
If the afterbirth did not come out on its own within the right time, it is important to call a veterinarian who will examine and note alarming symptoms:
- the animal looks tired and depressed, refuses food and water;
- the cow has a fever;
- the animal hunches, arches its back;
- there are regular attempts, similar to the urge to urinate;
- the cow's milk supply decreases.
When the afterbirth has not completely departed, and large pieces of the fetal membrane remain in the uterus, after 1-2 days they will begin to decompose due to the multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms inside the organ. The cow begins a mucous-bloody discharge, sometimes with an admixture of pus, with a sharp unpleasant odor.
Diagnostic measures
The veterinarian can diagnose that the afterbirth could not leave on its own according to the characteristic clinical picture. It is necessary to palpate the uterine cavity and vagina.
Treatment methods
Starting treatment in the early postpartum period, if the afterbirth has not separated on its own, will prevent negative consequences for the cow's health and will quickly have a positive effect. Quality care, feeding, and drinking plenty of clean water are important for the animal.
First of all, conservative therapy is used, aimed at the independent separation of the remnants of the placenta. It begins within 8-16 hours after calving. If childbirth was difficult, it is recommended to start drug treatment immediately, without waiting for complications. Only if it is ineffective is manual cleaning of the uterus indicated.
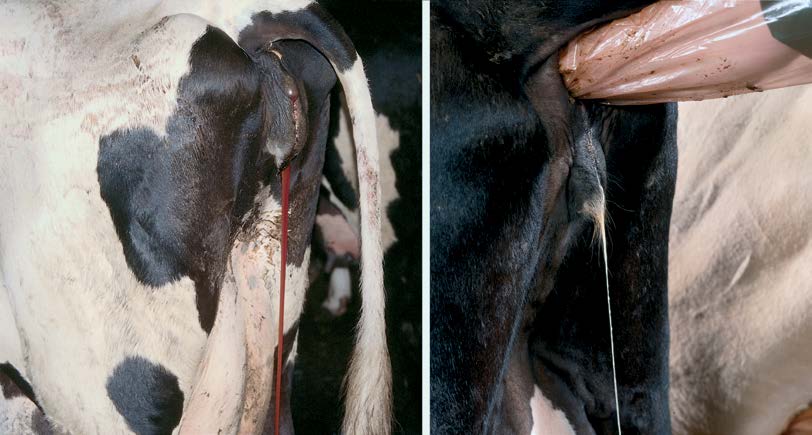
Operation
If the afterbirth still did not come out on its own within 16 hours after calving, and conservative therapy did not give positive results, it is necessary to manually select the placental tissue from the uterus. This should be done exclusively by a specialist. It is recommended to select the afterbirth 2-3 days after calving, since it will be problematic before, and the risk of postpartum hemorrhage increases.
You should not delay cleaning for longer either, since the decomposition of the membranes will cause general intoxication of the animal's body.
Even with a highly qualified veterinarian, he does not always manage to completely remove the remnants of the placenta, which is why in the future the cow has to be treated with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. After manual cleaning of the uterus, the animal is shown antibiotics administered inside the organ:
- Penocefur is a third generation antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. Forms a foam that destroys pathogenic microflora. Has a minimum number of side effects, does not affect the quality and quantity of milk;
- “Carotil” is an intrauterine antimicrobial agent with bacteriostatic and antioxidant properties. The substances that make up the drug help to reduce inflammation and accelerate tissue healing.
Immediately after the operation, it is important to prevent intoxication and administer to the animal intravenously 200 milliliters of 40% glucose and 200 milliliters of 10% calcium chloride solution. To improve discharge of lochia, rectal massage of the uterus can be done.
Medication
Even with the efforts of the veterinarian to remove the afterbirth completely, this is not always possible, which can lead to endometritis. Immediately after cleaning the uterus, 3-4 suppositories with disinfecting properties must be introduced into the organ cavity:
- "Iodopen";
- "Ginobiotic";
- "Metromax";
- "Nifumen";
- Enroflon.
Intrauterine drugs should be injected twice a day until the cervix is closed, making the use of such drugs no longer possible.
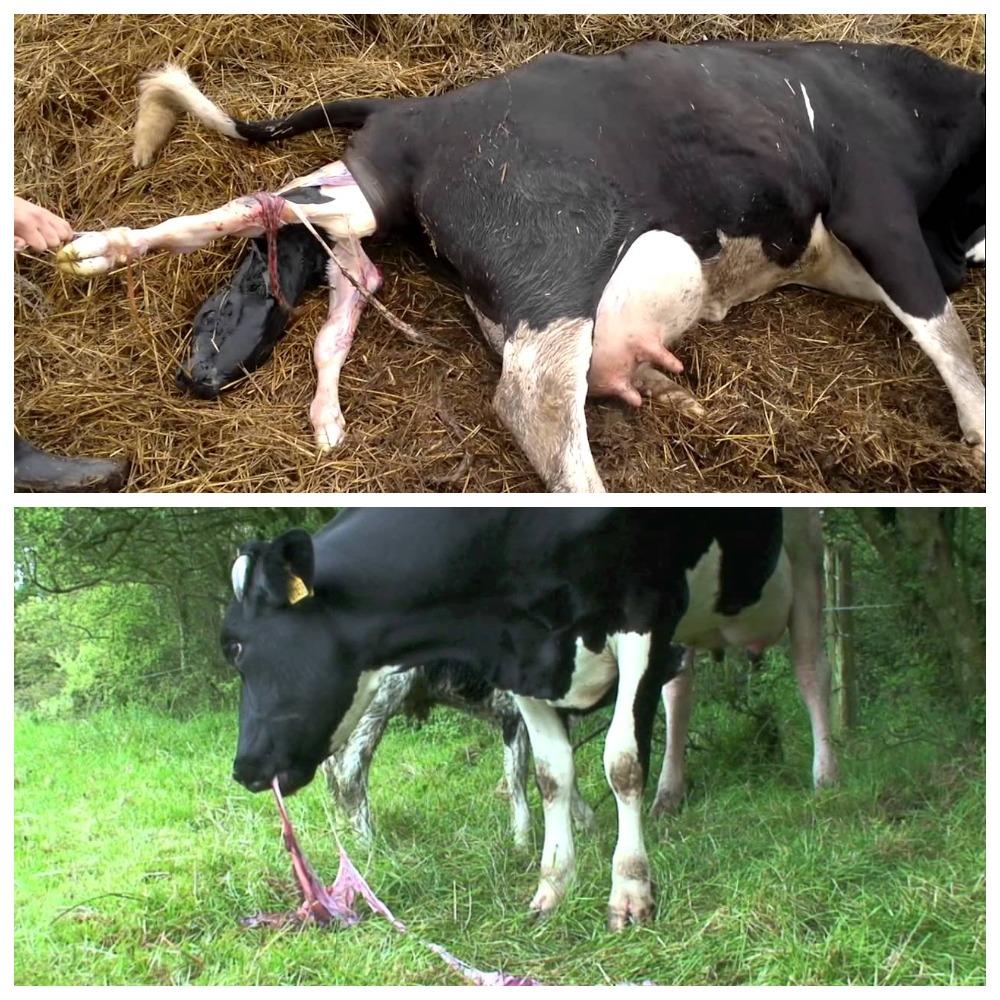

Ikhglukovit has a good antimicrobial effect - it is administered by injection, in addition to preparations in the form of suppositories and vaginal tablets. Single dosage - 40 milliliters, divided into two injections (20 milliliters on each side of the base of the cow's tail into the paravaginal tissue and pelvic cavity). The tool is used every other day until the fetid discharge disappears completely (on average, 7-10 days).
Hormonal agents
It is recommended to use hormonal drugs before manual intervention to cleanse the uterus, when the afterbirth is not separated on its own within the prescribed time. The main hormonal agent that helps in the discharge of the membranes is "Oxytocin". At a dose of 50 milliliters, it contributes to the contraction of the uterine muscles and the separation of the remnants of the placenta with their subsequent release.
Another effective hormonal drug is Magestrofan. The substance cloprostenol (a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin F2a) contained in it contributes to the rapid resorption of the corpus luteum formed during pregnancy and to an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus. Dosage for a cow is 3-4 milliliters 6-12 hours after calving.
The drug "Uterobag", used to improve the discharge of the placenta, contains propranolol hydrochloride, which affects endogenous oxytocin. An increase in hormone levels leads to uterine contractions and expulsion of the placenta. To achieve the effect, "Uterobag" is injected into the vein three times at intervals of 12 hours.
When the uterus cleans itself of the remnants of the placenta, liquid suppositories "Endometramag Green" are injected intrauterinely at a dosage of 150 milliliters. The tool effectively suppresses the viral, fungal and bacterial flora, preventing further infection of the uterus and the development of the inflammatory process.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are used to remove an acute inflammatory process in the uterus, accompanied by an increase in temperature in the animal, the release of fetid mucus with purulent blotches, as well as after manual cleaning of the uterus. Modern, safe for cattle products:
- Ceftiomax is a broad spectrum drug from the third generation cephalosporin group. Effectively acts on the most common causative agents of necrobacteriosis and causing the development of postpartum endometritis. The dosage is selected based on the body weight of the cow - 1 milliliter per 50 kilograms of weight. One injection is made per day, the course of treatment is 5-7 days;
- "Bicillin 3" is an antibiotic from the group of semi-synthetic penicillins. An adult cow is injected with 10,000 IU once every 3 days for two weeks;
- Ceftimag is a drug based on ceftiofur, a third-generation cephalosporin. If the placenta has not cleared off after calving, and endometritis has developed, the agent is administered once daily for 3-5 days at the rate of 1 milliliter per 100 kilograms of weight.

There is no need to try to give the cow an antibiotic in the form of tablets - the animal will not eat the bitter medicine, moreover, her condition may worsen by the development of digestive disorders and diarrhea.
Folk recipes
To make the afterbirth easier to separate, folk methods are also used if the owner of the cow does not have the opportunity to call a veterinarian for help:
- frequent milking of a cow - increases the level of oxytocin, which is responsible for the contractility of the uterus;
- feeding the animal with a sweet solution - 400 grams of sugar diluted in a liter of water (it is necessary for the cow to drink at least 2 liters of liquid);
- collecting amniotic fluid and drinking it for the cow - the substances present in the composition of the liquid increase the activity of uterine contractions and facilitate the discharge of the placenta.
In difficult situations, when the health and life of the cow is in danger, it is better not to use folk remedies, but to contact an experienced veterinarian for an emergency solution to the problem.
Possible consequences
With prolonged non-departure of the placenta, the cow may develop health problems in the future - the impossibility of insemination, infertility. If you ignore the dangerous symptoms, the animal develops endometritis - inflammation of the mucous tissue of the uterus of bacterial etiology, which can be complicated by mastitis. The therapeutic measures not taken for several days provoke further blood poisoning and can lead to the death of the cow.
Preventive measures
So that cows do not have problems with the discharge of the placenta, it is important to observe prophylaxis - to avoid causes that provoke weak labor and delay of the membranes. It is necessary to follow the correct diet, enriched with vitamins and minerals, graze animals daily, giving them the opportunity to move actively.
You can introduce additional portions of vitamin E by injection or as part of the feed, but not during the dry period, so as not to provoke placental abruption and oxygen starvation of the calf.
Delayed or incomplete discharge of the placenta is a common problem among cows, which, in the absence of timely treatment, negatively affects reproductive function. Prevention of labor disorders and high-quality complex therapy help prevent serious complications for the cow's health.