Causes and symptoms of obstruction of the esophagus in cattle, how to treat
Obstruction of a part of the esophagus in cattle often catches inexperienced owners by surprise. The disease develops rapidly, and any delay threatens the animal with death. Anxiety, strained cough, strong salivation signal an impending disaster. In such cases, the help of an experienced veterinarian is needed. The specialist will determine the reason for the deterioration of the pet's well-being and will provide emergency assistance.
What is it?
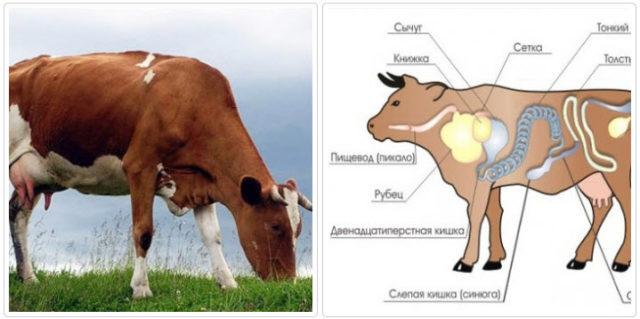
Primary upper gastrointestinal obstruction is an accidental occlusion of the animal's esophagus. A foreign body or large chunks of food act as a cork. An accident entails a complete or partial obstruction of the stomach. If the object is significantly larger than the lumen in the pet's stomach, the animal's esophagus begins to involuntarily contract. This mechanism was conceived by nature for self-disposal of the pet from foreign objects in the digestive tract. As a result of reflex actions, large chunks of food move along the excretory pathways of the digestive tract.
Unfortunately, a pet rarely manages to get rid of foreign objects in a natural way. In most cases, contractions of the upper stomach lead to inflammation of the walls of the esophagus, so it is impossible to delay the treatment of the animal.
Causes of obstruction of the esophagus in cattle
Accidental factors, serious illness or negligence of a person can serve as the cause of the dangerous phenomenon.
- Eating large pieces of pumpkin, root vegetables, unmilled corn cobs, large quantities of oil cake and other unsuitable food by animals. Such a nuisance often happens to hungry pets. Animals convulsively swallow food without rubbing it.
- Cows are often the victims of accidents. Horned pets need constant mineral feeding. Lack of additives leads to the ingestion of random items by cows.
- Sometimes a narrowing of the esophagus becomes the culprit of the stomach blockage. Pathology occurs due to damage to the walls of the stomach. Actively growing tumors lead to injury. The formations squeeze the digestive organ, and the lumen is completely blocked. Diseases of tuberculosis or leukemia lead to a similar effect. Numerous lymph nodes injure the stomach lining and block the gap.
- Paralysis of the esophagus often leads to disruption of the digestive tract. The collapse can be caused by rabies, central paralysis, or organ contusion.
Symptoms of the disease
Changes in pet behavior and well-being occur suddenly.
- The animal tries to make swallowing movements. Thus, the pet is trying to push the stuck lump further along the esophagus.
- Persistent urge to vomit.
- Strong salivation. Due to the lack of chewing gum, the pet continues to work with its jaws in vain.
- Convulsive, paroxysmal cough.
- The pet is worried, wags its tail, groans. Sometimes he tries to hit the abdomen with his limbs.
- If a foreign object gets stuck in the cervical esophagus, the affected area swells. A spherical seal is clearly felt in the region of the left jugular groove. After a few minutes, the swelling becomes inflamed and begins to hurt the animal.
- If the lumen is only partially blocked, the pet may drink water and regurgitate accumulated gases. In case of complete blockage of the digestive organ, gases accumulate in the animal's body. In this case, the pet develops tympania.
- Some individuals, even with a complete overlap of the organ, try to eat and drink water. Unable to seep through the esophagus, the liquid rushes back and splashes out through the pet's nasal passages. The same story happens with food. However, in this case, food can settle in the stomach above the covered area.
Rules for treating a cow
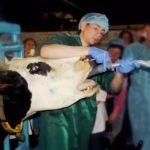
To determine an accurate diagnosis, the cow is examined. First of all, a specialist examines the jugular groove and determines the degree of enlargement and swelling of the organ. The doctor carefully probes the pet's neck, passing his fingers along the entire length of the jugular groove. Thus, a random object is found stuck in the upper part of the esophagus.
In other cases, the sensing method is used. The tool is selected in accordance with the weight of the animal. The procedure allows you to push the trapped foreign body and release the accumulated gases outside. In difficult cases, veterinarians resort to x-rays or esophagoscopy. If the upper stomach is completely blocked, emergency intervention is necessary. Otherwise, the cow will die from asphyxiation. Treatment methods depend on the location of the foreign body in the pet's digestive tract.
In order to remove the stuck object, the cow is securely tied to a support or tree. During the procedure, the mouth of the animal must remain open, therefore, a spacer is inserted between the teeth of the pet - a wedge. The foreign body is removed from the cow's esophagus using a towel-wrapped hand or probe. Using the tool, the object is pushed to the excretory tract of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is done with caution, otherwise the stomach can be injured.
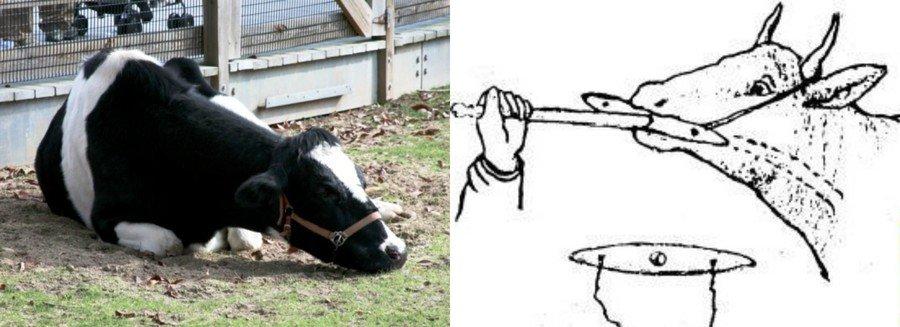
In mild cases, the stuck object is removed by vomiting. For this, the pet's neck is stroked in the area of the jugular groove. Hands move towards the head of the cow. Thus, the gag reflex is activated. To facilitate the procedure, the cow is given 0.5 cups of vegetable oil.
In extremely severe cases, a surgical operation (esophagotomy) is performed.
Folk remedies and recipes
After removing the foreign object, the pet's digestive tract needs help. The tried and tested folk methods will help to establish the work of organs:
- A decoction of chamomile, yarrow or flax seed. To prepare the product, 25-30 g of herbs are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. The drink is simmered in a water bath for 30 minutes. After cooling, the product is filtered and given to the pet for 2 days.
- In some cases, a gentle massage of the hungry fossa helps to cope with the problem. The procedure is done with a fist.
- Yeast drink. To prepare the product, 150 yeast is dissolved in 1.5 cups of warm boiled water and left to infuse for 30 minutes. Meanwhile, mix 0.5 cups of vodka and 100 g of sugar.Yeast infusion is added to the resulting mixture. As a result of cooking, 1 liter of the potion is obtained. The medicine is given to the animal a couple of times a day. The course of treatment is designed for 2 days. It should be remembered that the yeast drink is given to the pet only after removing the foreign object from the esophagus.
Why is blockage dangerous?
A blockage in the upper stomach is fatal to the animal. In case of untimely assistance, the animal develops inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, swelling of the scar and tissue necrosis. The rapid development of the disease leads to pneumonia, heart compression and asphyxiation. If rescue measures are taken within the first hours, the accident can be prevented.
Prevention
Responsible animal feeding helps avoid problems. Competent farmers do not allow horned pets to graze near potato and beetroot fields. Large root crops and corn cobs intended for animal feeding must be crushed. The pasture and the place where livestock are kept are regularly inspected. All foreign objects are removed. The diet of animals must include vitamin and mineral supplements. A special licking salt is placed in the trough.